
© Copyright NINGXIA YI PIN PU TRADING CO., LTD. All rights reserved.
REPUBLIC OF SERBIA
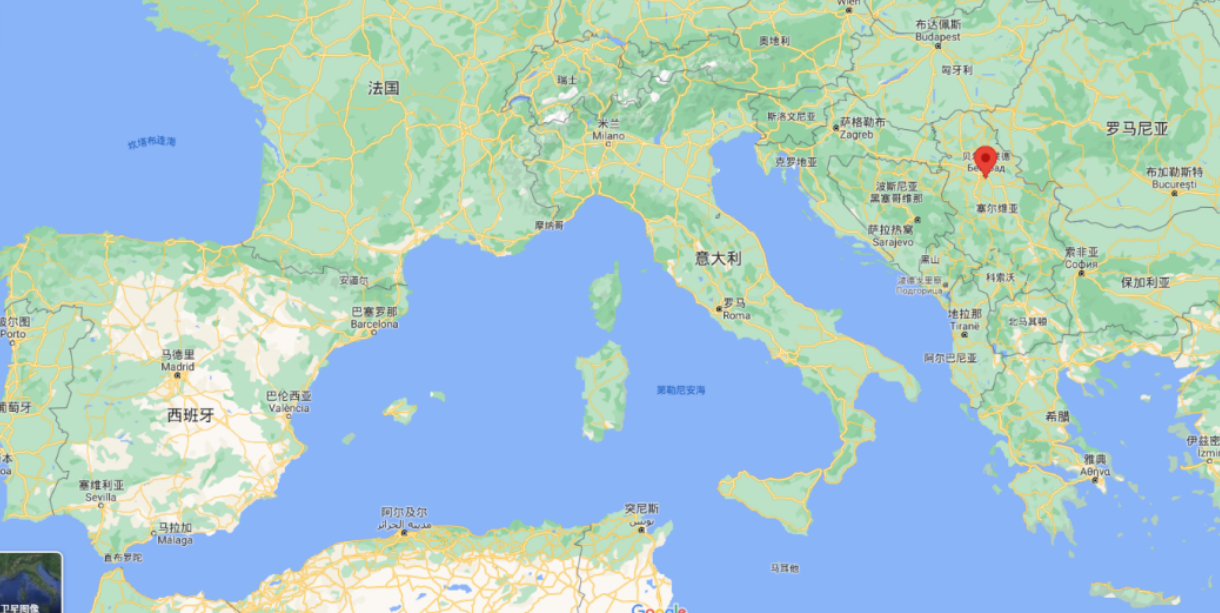
The Republic of Serbia is located on the border of Central and South-eastern Europe in the southern Pannonian Plain on the Balkan Peninsula. It borders Hungary to the north, Romania to the northeast, Bulgaria to the southeast, northern Macedonia to the south, Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina to the west, and Montenegro to the southwest. In the south and southwest, it borders Albania through the disputed territory of Kosovo. The way which must be passed is to crossroads between Europe and Asia, the Middle East and Africa, which is called the crossroads of Europe in Serbia. The population of Serbia is approximately seven million, without Kosovo or 8.7 million if the territory is included. The capital of the Republic of Serbia is Belgrade, it is one of the largest and oldest cities in Southeast Europe. The territory of the Republic of Serbia, including Kosovo, is 88,361 km2, and without Kosovo it is 77,474 km2.
Administrative divisions:
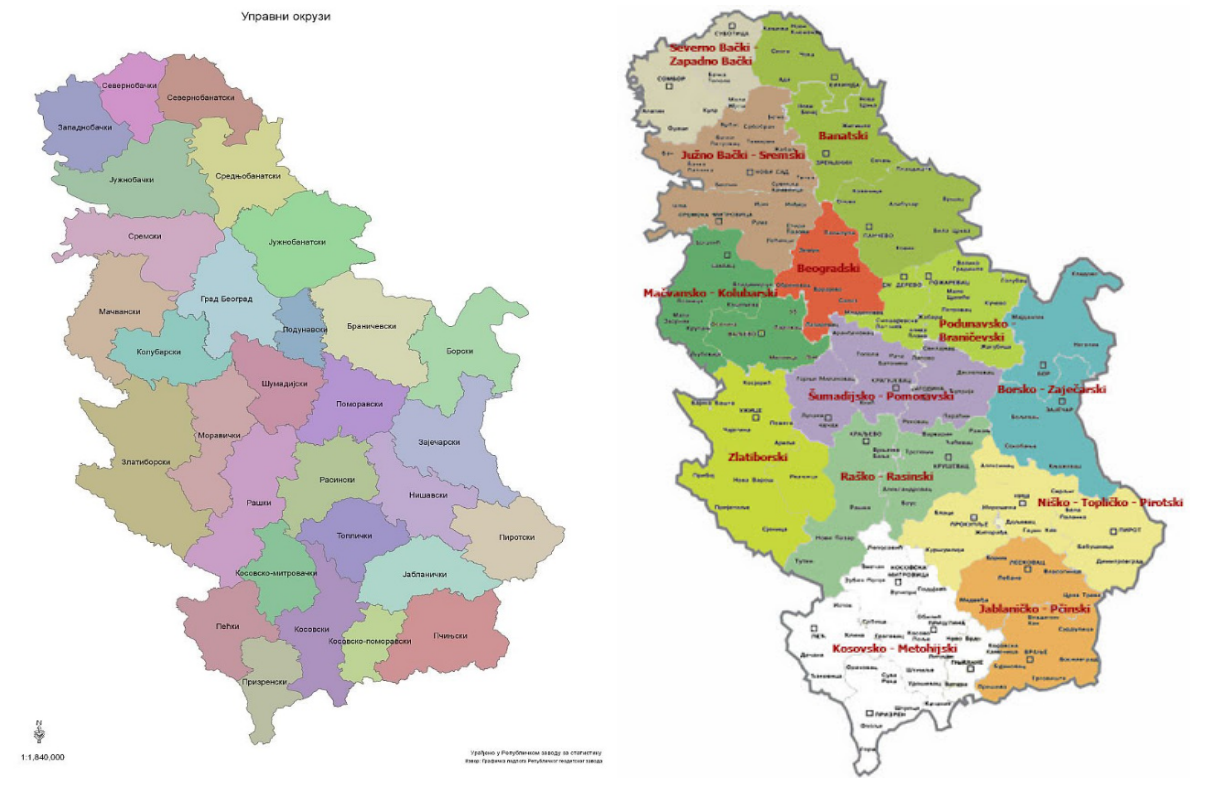
Districts of Serbia
Administrative districts are the largest subjects of the regional division of the Republic of Serbia and are composed of municipalities and cities. Administrative districts are regional centres of state power; they represent a purely administrative division and are the seats of various state institutions.
Serbia is divided into 29 administrative districts, of which 7 are located in Vojvodina, 9 in Southern and Eastern Serbia, 8 in Sumadija and western Serbia and 5 in Kosovo and Metohija, while the capital of the Republic of Serbia, the City of Belgrade, represents its own administrative district.
Municipalities and cities are the level of administrative division of Serbia. The country is divided into 145 municipalities ( 38 in Southern and Eastern Serbia, 42 in Sumadija and Western Serbia, 37 in Vojvodina and 28 in Kosovo and Metohija) and 29 singular cities ( 9 in Southern and Eastern Serbia, 10 in Sumadija and Western Serbia, 8 in Vojvodina and one in Kosovo and Metohija), forming the basic level of local government.

Climate environment
The Serbian climate is between a continental climate in the north, with cold dry winters, and warm, humid summers with well distributed rainfall patterns, and a more Mediterranean climate in the south with hot, dry summers and autumns and average relatively cool and more rainy winters with heavy mountain snowfall.
Resources
The natural resources found on the territory of Serbia include coal, iron ore, oil, gas, gold, silver, copper, zinc, antimony, chromite, magnesium, pyrite, limestone, and marble. The estimated value of mineral reserves in Serbia is more than 200 billion euros.

Serbia has very favourable natural conditions (land and climate) for a variety of agricultural production, experienced producers, the best experts and scientists, as well as the world recognizes the selection of numerous crops. The most important agricultural products of Serbia are corn, wheat (flour), sunflower (oil and meal), sugar beet (sugar), soy (oil and protein products), potatoes, raspberries, apples, plums, cherries, grapes, pork, beef and poultry. meat as well as milk.

Population
The current population of Serbia is 8,704,761 as of June 5, 2021. Serbia population is equivalent to 0.11% of the total world population. Serbia ranks number 99 in the list of countries (and dependencies) by population. The population density in Serbia is 100 per Km2 (259 people per mi2). 56.2 % of the population is urban (4,913,067 people in 2020).
Economy
Data from the National Bureau of Statistics
It is estimated that the total economic activity in the Republic of Serbia in 2020, measured by the real movement of gross domestic product (GDP), recorded a decline of 1.1% compared to 2019.
Agricultural production achieved a growth of physical volume of 4.4% in 2020, while industrial production, in the same period, recorded an increase in physical volume of 0.2%. Turnover in retail trade was a real growth of 5.0%, while turnover in wholesale trade was nominally reduced by 6.1%. Earnings without taxes and contributions in 2020, compared to the previous year, are nominally higher by 9.4%, and really by 7.7%. The annual inflation rate is 1.2%.
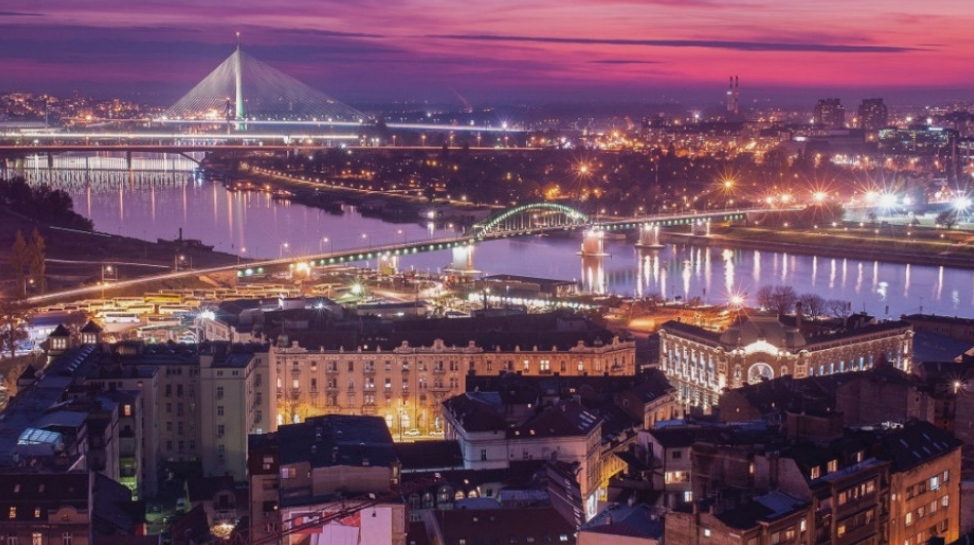

Tourism
The north of Serbia is a vast plain of the Pannonian Plain, swamps and rivers, forests and meadows, and the south by wild forests, high mountain ridges, lakes, caves and fast cold rivers. Thanks to numerous positive development trends, the tourism industry has become one of the most dynamic and propulsive industries, provides a strong generator function in a wide range of activities, which is increasingly included in the priorities of economic development of many receptive countries and their individual parts.
Urban tourism in Serbia
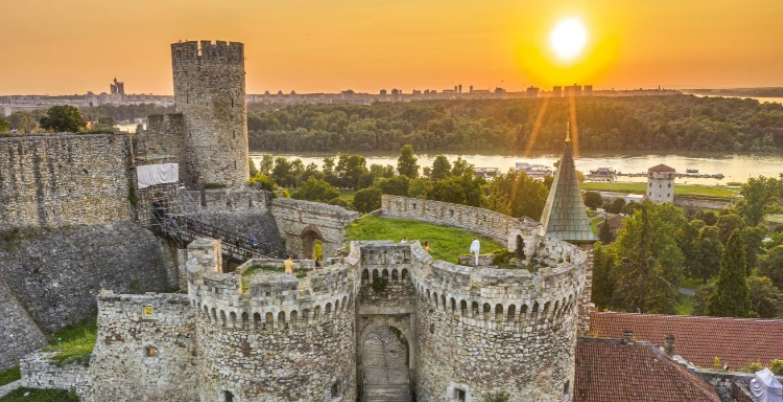
Belgrade
As the capital and largest city of Serbia, Belgrade abounds in cultural and historical monuments. The nightlife in Belgrade is famous in this part of Europe. It is one of the oldest cities in Europe, whose past can be traced back to the Old Century.

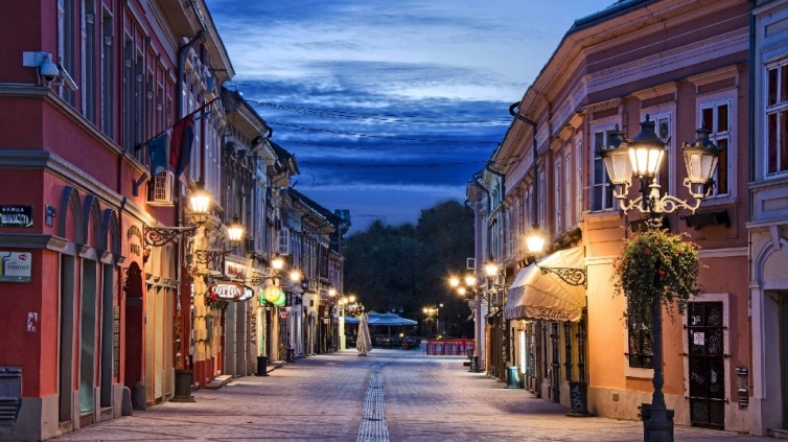
Novi Sad
Since the Turkish occupation of Serbia, Novi Sad, as a free royal city in Austria-Hungary, has been the centre of Serbian culture in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. The city was known as Serbian Athens. One of the world's largest music festivals, EXIT, is also held in this city.

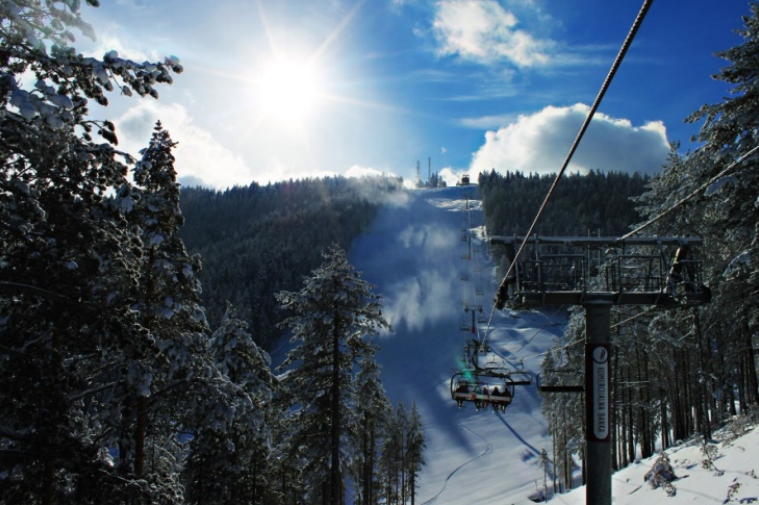
Mountain tourism in Serbia
The mountains of Serbia are divided into the Rhodope, Carpathian-Balkan and Dinaric mountains. These mountains are home to various indigenous and endemic species. It is possible to enjoy the charms of the mountain in summer and winter. Full of fast rivers, clear streams and crystal lakes, these natural beauties reveal a different side of their charms at any time of the year.

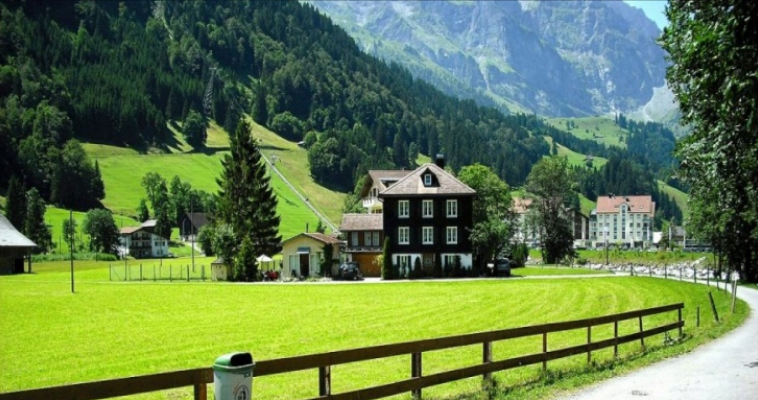
Countryside tourism
Serbia has excellent conditions for the development of rural tourism. Serbia can earn several billion euros a year from rural tourism. Well-known tourist villages in Serbia are: Sicevo, Sirogojno, Gostilje, Mokra Gora, Kostunica. Thanks to the rich rural tradition, one of the most important potentials of Serbian rural tourism is the development of ethno villages. The most famous ethno-villages in Serbia are Staro selo in Sirogojno, Drvengrad in Mokra Gora and Kostunica.

Spa and climate tourism
More than 1000 sources of thermo-mineral waters in Serbia are a real national treasure, on which about fifty spas have sprung up. Spas are natural centres of wellness and spa therapy increasingly popular in this modern time.
Industry
Serbia's main industrial sectors include: automotive, mining, non-ferrous metals, food-processing, electronics, pharmaceuticals, clothes. Serbia has 14 free economic zones as of September 2017, in which many foreign direct investments are realised.